

As you can see, the result set doesnot always have to be an array of objects:

We use ithere to return a statement for every user. age )ĬONCAT() is a function that can join elements together to a string. It is also possible to compute new values: The user name isreturned as userName instead of name, the age keeps the attribute key inthis example: The query defines the output format for every user document. Let’sinsert a second document using a modification query: There is another type of query called data modification query. This type of query is called data access query. DOCUMENT() is a function to retrievea single document or a list of documents of which you know the _keys or _ids.We return the result of the function call as our query result, which is ourdocument inside of the result array (we could have returned more than one resultwith a different query, but even for a single document as result, we still getan array at the top level). The result appears below the query editor:Īs you can see, the entire document including the system attributes is returned.
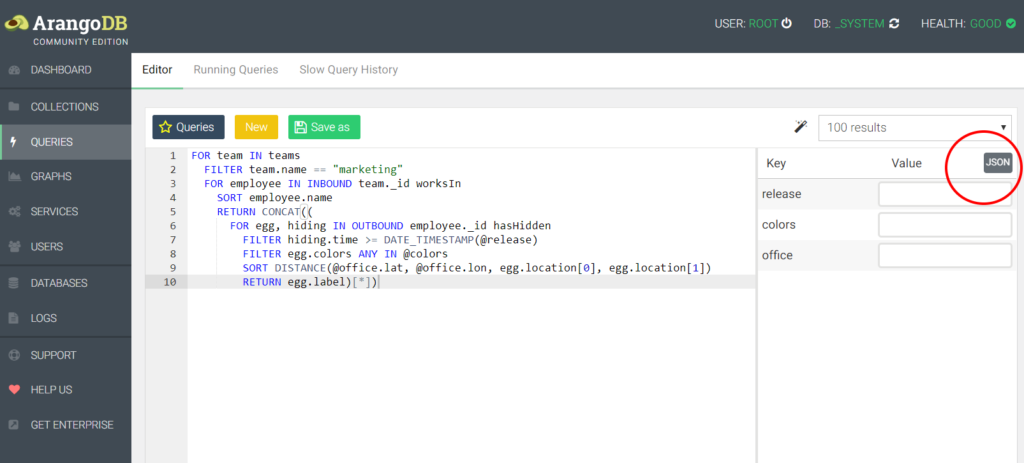
Click the _QUERIES menu entry to bring up the query editorand type the following (adjust the document ID to match your document): We candirectly look up the document we created via the id, but there are alsoother options. Time to retrieve our document using AQL, ArangoDB’s query language.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
